

Following the road laid out by EV regulations is anything but straightforward. The road is filled with twists and turns along the way – not to mention new speed bumps from recent rule changes and ongoing regulatory developments. If the current state of electrification regulations and what’s needed to comply leaves you scratching your head, this guide will help point you in the right direction to start your transition to EV fleets.
As the current administration continues to walk back previous regulatory strides made towards electrification, EV regulations remain unpredictable in the near-term at the federal level. However, states are leading the charge, implementing EV-focused policies aimed at improving public health, reducing air pollution, and mitigating climate change.
State Actions to Accelerate the EV Transition
Back in 2020, a bipartisan group of 15 state governors plus the District of Columbia came together to sign a Memoriam of Understanding, committing to a goal of 100% of all new medium- and heavy-duty vehicle sales be zero emission vehicles by 2050, with an interim target of 30 percent zero emission vehicle sales by 2030 (Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management). While this promising multi-state collaboration to reduce vehicle emissions remains intact, several US states continue to go above and beyond federal requirements and drive electrification forward by participating in the following group electrification initiatives:
Drive to Zero (CALSTART):
- An international program and campaign which aims to accelerate the growth of global zero- and near-zero-emission (ZE) commercial vehicle space with a goal of reaching 100% new zero-emission medium- and heavy-duty vehicle sales by the year 2040.
- Drive to Zero is built upon the Beachhead Strategy developed in partnership between CALSTART and the California Air Resources Board (CARB). The Beachhead Strategy identifies the commercial vehicle market segments where zero- and near-zero technologies are most likely to succeed and help drive growth in other segments.
- Several US state and city governments and organizations have signed CALSTART’s Drive to Zero pledge, including the New York State Energy Research & Development Authority (NYSERDA), the New York City Economic Development Corporation (NYCEDC), the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey (PANYNJ), the California Air Resources Board, Bay Area Air Quality Management District, New York City, and Los Angeles.
The West Coast Clean Transit Corridor Initiative:
- An ongoing, collaborative effort among 16 utilities across California, Oregon, and Washington, to support the development of electric vehicle charging facilities along I-5, from San Diego to British Columbia, for heavy- and medium-duty freight haulers and delivery trucks.
- Following an initial June 2020 report outlining conceptual charging sites, the West Coast utilities are conducting grid readiness assessments in preparation for infrastructure installations and upgrades that will support vehicle charging capacities of at least 3.5 megawatts with potential for further upgrades to create even higher-power sites.
- Organizations interested in partnering with utilities to build or upgrade their sites along the I-5 corridor are encouraged to connect with the appropriate utility.
Regional Electric Vehicle Plan for the West (REV West):
- An initiative launched by governors from Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming to develop an Intermountain West Electric Vehicle (EV) Corridor with the goal of supporting a seamless electric vehicle (EV) driving experience along key driving corridors in the intermountain west.
- Through the imitative, State energy offices and departments of transportation collaborate with utilities and private sector stakeholders to voluntarily expand EV corridors, harmonize signage and charging standards, and support public fleet electrification.
Midwest Regional Electric Vehicle (REV Midwest):
- A coalition formed by the governors of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin, designed to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles and deployment of charging infrastructure.
- Governors signed a non-binding MOU to coordinate on regional EV infrastructure strategies and siting to spur medium and heavy-duty fleet electrification, evaluate challenges and opportunities of manufacturing, and identify disadvantaged communities to ensure an equitable transition
State-Specific EV Regulations
In California, transportation is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for 39% of the state’s total emissions (California Air Resources Board). California’s overall philosophy to combat these emissions is by incentivizing low-emission and zero-emission fuels and batteries, as shown through the previously mentioned introduction of the ACC II and ACT regulations adopted by other states as well as these additional state regulations:
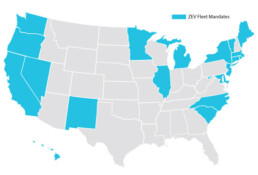
Advanced Clean Fleets (ACF):
- A California regulation designed to complement ACT by requiring fleets operating in California to transition to zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs), with compliance varying based on truck type, use, and fleet size.
- In January 2025, CARB withdrew its request for a federal waiver from the U.S. EPA that would have allowed the enforcement of the ACF regulation on private and federal fleets. Despite the waiver withdrawal, CARB maintains that the ACF provisions applicable to state and local government fleets remain in effect, as these do not require federal approval. Consequently, California state and local government fleets are still obligated to comply with the regulation’s requirements:
- All new vehicle purchases by covered government fleets must be zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs), unless an exemption applies.
- Fleets must gradually electrify their vehicles over 8500 lbs GVWR until the full medium-duty and heavy-duty fleet is made up of zero-emission vehicles by 2040
- Fleets must submit annual compliance reports to CARB, including vehicle inventories and ZEV procurement plans.
- As of 2025, drayage and commercial fleets are no longer mandated to comply with ACF due to regulatory rollback, but voluntary participation is encouraged.
Several additional states have introduced or expanded their own EV regulations:
- New York adopted its own Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Fleet Regulation, requiring all new light-duty state fleet purchases to be zero-emission by 2027 and full fleet transition by 2040. The state also passed an Electric School Buses mandate.
- Oregon enhanced its ACT implementation by adding ZEV procurement targets for public fleets, effective 2026. These targets require manufacturers to sell increasing percentages of ZEVs in the state each year: Keeping records of fleet emissions and energy usage
- Illinois created an EV Rebate Program under the Climate and Equitable Jobs Act (CEJA), which aims to have 1 million EVs on the road by 2030, supported by rebates of up to $4,000 for new and used electric vehicles, and $100 million in rebates for EV fleet purchases and charging stations. Planning: Ensuring your facilities are ready to support EV charging.
Do I Have to Comply? The Benefits of Early Action
While compliance deadlines may seem distant, transitioning early offers several advantages:
- Securing Incentives & Grants: Early adopters may qualify for state and federal funding, lowering the cost of EV purchases and infrastructure upgrades.
- Lower Operating Costs: EVs typically offer reduced fuel and maintenance expenses compared to combustion-engine vehicles.
- Regulatory Certainty: Planning ahead avoids the financial and logistical burden of last-minute compliance.
What You Need to Comply
Transitioning your fleet requires planning, data collection, and documentation. Compliance measures often include:
- Vehicle Inventory Assessment: Identifying which vehicles must transition and when.
- Emissions & Mileage Tracking: Keeping records of fleet emissions and energy usage.
- Infrastructure Planning: Ensuring your facilities are ready to support EV charging.
- Regulatory Filings: Submitting required reports to agencies like CARB or your state’s environmental agency.
Next Steps: Building Your Roadmap
The ever-changing nature of EV regulations can make the electrification process seem complicated, but with the right partner it doesn’t have to be. At ForeFront Power, our expert team can help you assess your compliance requirements, explore funding opportunities, apply for grants to claim funding, develop a phased transition plan, and streamline your fleet electrification journey.
Contact us today to learn about available exemptions, key regulatory considerations, and the best strategy for electrifying your fleet!

Interested in learning more?
We would love to discuss how our solutions might be a fit for your organization. Contact one of our solar, storage, or e-mobility experts today:







